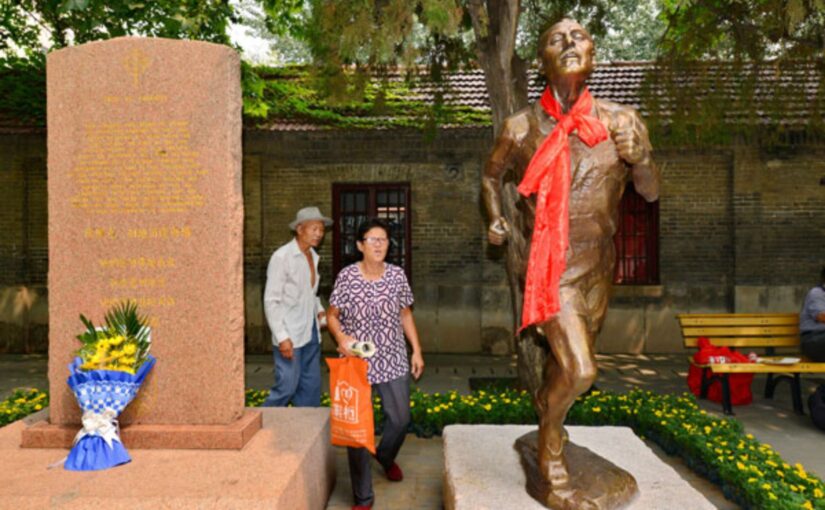During his recent visit to China for the commemoration of the 80th anniversary of the Chinese people’s victory in the war of resistance against Japanese aggression and the world anti-fascist war, our co-editor Keith Bennett participated in an international symposium organised by the Institute of Party History and Literature of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee, the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences and the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) Academy of Military Science, on September 2, and the Chinese Modernisation Forum (2025), organised by the School of Marxism, the Institute of Chinese Communist Party History and Party Building, and the Institute of Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, all of Tsinghua University, on September 4.
We print below the text of the paper presented by Keith, which outlines the solidarity extended by people in Britain to the Chinese people’s heroic resistance, from internationalists like George Hogg who made the journey to China, to the China Campaign Committee which organised and agitated the length and breadth of the country, to the singular contribution of the South Wales miners.
During his state visit to the United Kingdom in 2015, the 70th anniversary year of victory in the global anti-fascist war, in a speech in Buckingham Palace, President Xi Jinping recalled how our two countries had once stood together as allies and fought shoulder to shoulder.
Saying that the Chinese people would never forget this help during their hard time, he mentioned one individual in particular.
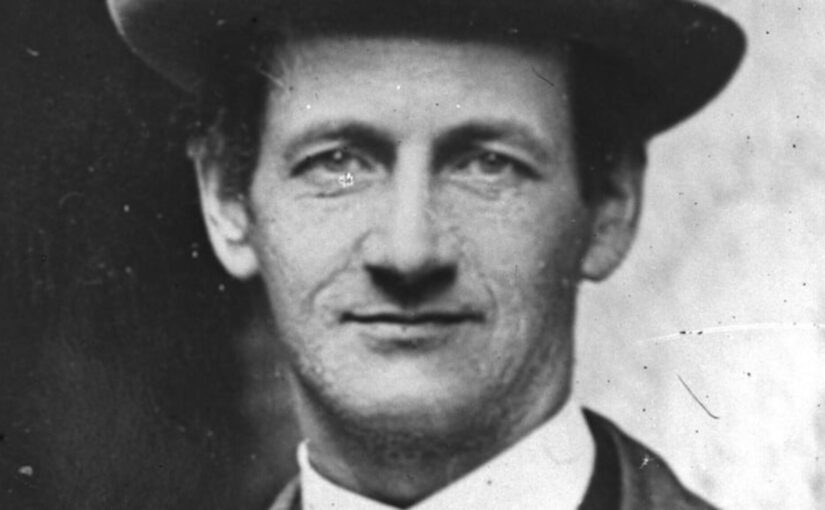
George Hogg died of tetanus aged just 30 on 22 July 1945 after devoting the last nearly eight years of his tragically short life to the Chinese people and their struggle for liberation, initially as a journalist and finally as headmaster of the Shandan Bailie School, caring for children orphaned by Japan’s brutal war of aggression.
He is perhaps best remembered for leading his pupils on a month-long 1,100 kilometre (700 miles) journey, most of it on foot and over snow covered mountain paths, to the relative safety of Gansu.
Long acclaimed as a national hero in China, Hogg remained almost entirely unknown in his native country for decades.
This began to be partially rectified with the 2008 publication of James MacManus’s biography, ‘Ocean Devil’.
The same year saw the release of the perhaps overly fictionalised feature film, ‘The Children of Huang Shi’, also called ‘Children of the Silk Road’ or ‘Escape from Huang Shi’, starring Jonathan Rhys Meyers as Hogg and Chow Yun-fat as the legendary Chinese communist Chen Hansheng.
George Hogg came to China as a young idealist. Although from a privileged background, he had a strong family background in pacifism, specifically in the Fellowship of Reconciliation, and rooted in non-conformist Christianity. However, he not only served China. His world outlook was transformed by China, as is well expressed in the title of his book, ‘I see a new China’.
In his 1954 book, ‘The People have Strength’, his mentor, the New Zealand internationalist Rewi Alley wrote:
“The sixty-odd peasant and refugee kids who carried him out to his grave in what has now become a playing field in a school training new technicians for a new China, will not forget the day. For them it meant the passing of a comrade who was very close to them. It is not given to everyone to live with heroic disciplined revolutionary armies. George had had inspiration from his tour, as correspondent, with the Eighth Route Army and then he came at my bidding, to work with Gung Ho [the Chinese Industrial Cooperatives], where there was little glory, many problems and a simple grave at the end of the trail.
“As he fought with tetanus in his last days of the summer of 1945, he asked to have the ‘Communist Manifesto’ read to him. I read it and he said, ‘That makes sense.’”
Whilst there were also other British friends who made their contribution to China’s struggle against Japanese militarism in China itself, such as Michael Lindsay, later 2nd Baron Lindsay of Birker, whose expertise in radio engineering was much appreciated and personally commended by Mao Zedong, and the Friends Ambulance Unit, organised by the Quakers and composed of conscientious objectors, roughly 200 of whom, with the British contingent being the largest group, served in China, including by providing medical supplies to the Shandan Bailie School, this was obviously an option that was open to relatively few.
But the solidarity of people in Britain with China’s war of national salvation, as a vital, and the first, front of the world peoples’ struggle against fascism was by no means confined to those who made that journey.
By far the most important and effective organisation in this regard was the China Campaign Committee (CCC), which was founded in late August or early September 1937, that is scarcely two months after the July 7 Lugou ‘Marco Polo’ Bridge Incident that heralded Japan’s full-scale invasion and the start of China’s nationwide resistance.
Seven days later, on July 14, the Daily Worker, the newspaper of the Communist Party of Great Britain (CPGB), described this as a “plain case of aggression” in its editorial, adding: “The Chinese people must be backed up.”
In an August 20 resolution passed by its Executive Committee, the CPGB stated: “The cause of peace throughout the world depends to a considerable extent upon the success of the heroic Chinese people… Unless peace forces can be rallied the Japanese attack on Central China will be followed by a German fascist outbreak in Central Europe… The defence of China is the defence of peace.”
Although it operated on an unprecedented scale and with unprecedented breadth of support, the China Campaign Committee did not emerge from a void or a vacuum.
Jenny Clegg, writing for the Society for Anglo-Chinese Understanding (SACU), noted that the “roots of this activism are to be found in Chartist opposition to the first Opium War” and refers to the ‘Hands off China’ Campaign (1925-27) and the ‘Friends of the Chinese People’ (1927-37), founded by the British Section of the League Against Imperialism.
Her father, Arthur Clegg, who served as the CCC’s National Organiser practically from the campaign’s inception, in his memoir, ‘Aid China – 1937-1949’, published in 1989, traces the roots of such solidarity back even further:
“Movements like the China Campaign Committee have long been part of the democratic tradition in Great Britain. They date back to the English Revolution [of the 1640s] when the Levellers took a stand for Irish independence and the end of English interference in Ireland.”
Arthur Clegg details the extraordinary range of forces mobilised by the CCC. They included church and missionary societies, businesses, some of the leading intellectual and cultural figures of the time, members of the House of Lords, the Chinese community, people with a specialised interest in China and Chinese culture, and many others.
On one occasion he even personally received a financial donation from a Colonel Younghusband. Only years later did he realise that it was the same Younghusband who had led the 1905 British invasion aimed at separating Xizang (Tibet) from the rest of China. He writes: “The only explanation I can find was that he was trying to make amends for his past efforts to weaken China.”
Support was forthcoming from many members of the Labour and Liberal parties and even from the occasional Conservative MP. However, Clegg is at pains to point out:
“Our greatest and most consistent supporter was the Communist Party, both directly and indirectly, for in those days it had influence far beyond its small but increasing membership. It was the first party to take a position defending China, the first to issue a pamphlet for China, the first to organise a Hyde Park meeting, where on August 23 [1937], J.R. Campbell demanded a Japanese withdrawal. Its branches and members loyally supported our meetings, distributed our handbills, posted our posters and saw in this a reinforcement for, rather than any rivalry with, the similar work they were doing for Spain. We all knew the issue of Spain and the issue of China were one and the same, the issue of preventing a world war.”
A clear example of how such direct and indirect support worked in practice is provided by the South Wales miners.
Continue reading Shoulder to shoulder: British people’s solidarity with the Chinese People’s War of Resistance Against Japanese Aggression