Interviewed by the Global Times, Erik Solheim describes the West’s accusations of Chinese “overcapacity” in relation to solar energy and electric vehicles as “a complete failure”.
From the perspective of combatting climate change, China is doing crucial work and blazing a trail that others should follow: “We have all called for many more high-quality green products from everyone, from China, from Europe, from the US, from everyone. Why start blaming China for doing what is expected from everyone?”
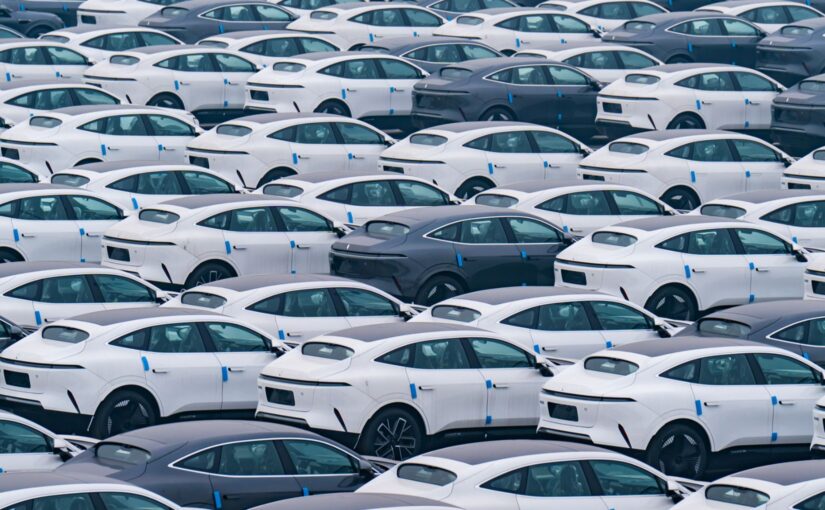
Solheim further notes that, from an economic perspective, accusations of overcapacity make little sense, “because what creates the foundation for trade is overcapacity… My nation, Norway, for example, is a big exporter of salmon… We raise and produce much more salmon than we can eat ourselves. Then we sell some to others. And then, for instance, we can import electric cars from China… We should not fear overcapacity, but we should turn it into a mutual benefit where everyone benefits from Chinese leadership in electric cars as they benefit from our production of salmon.”
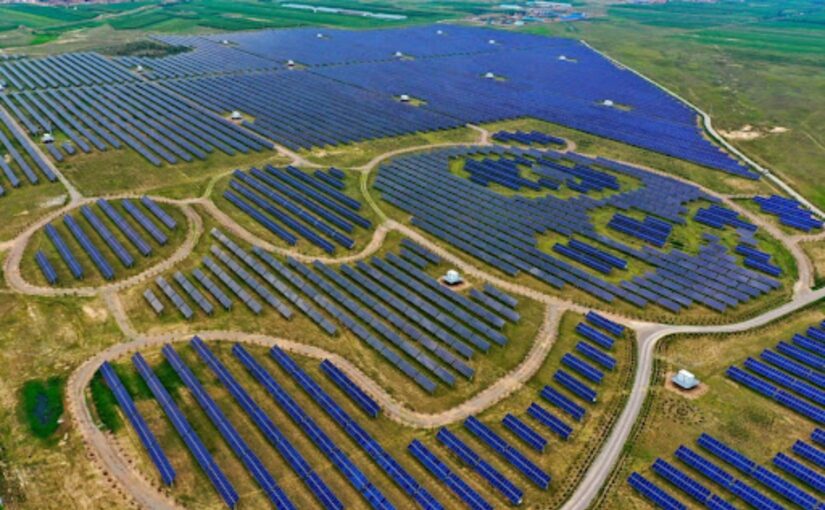
Ultimately, tariffs will slow down the green transformation “because China is now the indispensable country for everything green”, given that “60 percent of all green technologies in the world are in China” and “when it comes to solar energy, maybe the figure is even more than 90 percent.”
Solheim also describes some of China’s contribution to sustainable development in the Global South: “I was living in Kenya for quite a number of good years. In Kenya, China has constructed the Mombasa-Nairobi railroad, which goes through some very vulnerable ecological areas. But it is the cleanest and most well-functioning transport system in Kenya. It’s an absolute, wonderful, green contribution to Africa.”
Erik Solheim is former under-secretary-general of the United Nations and former executive director of the UN Environment Programme. He spoke at our event Building a multipolar world – Ten years of the Belt and Road Initiative in November 2023.
GT: During your recent visit to China, you posed a photo of your morning run. What was it like to go for a morning run in Beijing?
Solheim: It was absolutely wonderful. The sun was bright, the sky was blue. You could breathe in the fresh air. It was a nice experience and highlighted a contrast to 10 years ago when the air pollution was thick and the sky was gray. It’s such enormous progress in such a short time. There is more to be done. But China has largely won the war against pollution.
GT: In the same tweet, you mentioned: “Why doesn’t the world start competing and stop complaining about China’s green leadership?” They are complaining about China’s “overcapacity.” Do you think China has an issue of “overcapacity”?
Solheim: I think the narrative of capacity is a complete failure for two reasons.
First, this is exactly what we all have wanted. This is even what the Joe Biden administration in the US has called for. We have all called for many more high-quality green products from everyone, from China, from Europe, from the US, from everyone. Why start blaming China for doing what is expected from everyone? A few years ago, the West was complaining that China’s production was emitting too much pollution. And now they’re complaining that China is making green products.
Second, this is complete nonsense from an economic perspective because what creates the foundation for trade is overcapacity. If the US had no overcapacity in its industries for the last 100 years, it would not have become a great nation. It became great because it had overcapacity – it could produce for global markets.
My nation, Norway, for example, is a big exporter of salmon. Why? Because we have overcapacity for salmon. We raise and produce much more salmon than we can eat ourselves. Then we sell some to others. And then, for instance, we can import electric cars from China. One of the most valuable companies in the world today is Apple, an American company. Why? Because they have an overcapacity in electric smartphones. Otherwise, they would have just been in the American market and they would have been a small company. We should not fear overcapacity, but we should turn it into a mutual benefit where everyone benefits from Chinese leadership in electric cars as they benefit from our production of salmon.
GT: Are there any green cooperation projects between China and other countries that have impressed you? What are the positive impacts of those projects?
Solheim: Absolutely. Two months ago, I was in Bangladesh, where China had constructed a bridge called the Padma Bridge. It is a wonderful rail and road bridge across the Padma River. That one bridge increased the GDP of Bangladesh by 1 percent because it connects the eastern and western parts of the land. That is a wonderful support for Bangladesh.
I was living in Kenya for quite a number of good years. In Kenya, China has constructed the Mombasa-Nairobi railroad, which goes through some very vulnerable ecological areas. But it is the cleanest and most well-functioning transport system in Kenya. It’s an absolute, wonderful, green contribution to Africa.
GT: Some observers suggest that the US doesn’t want to live in a world where the world’s foremost energy provider is China, so they’re making huge efforts to catch up and, at the same time, attempt to slow China down with initiatives like this “overcapacity” rhetoric. What’s your take on this view?
Solheim: I think there are two aspects to this view.
First, the US is deeply concerned about having a peer competitor, such as China. For the past century, the US has been the dominant global power, or the only dominant power in the world, and it’s not used to sharing that position. However, it needs to get used to the reality that China’s economy will surpass that of the US, and China will play an increasingly important role in global affairs. Additionally, the US doesn’t only need to adapt to the rise of China, but also to the rise of other powers like India, Turkey, Indonesia, and Brazil. The era of US dominance is over, and it needs to adapt to the change.
On the other hand, President Biden wants jobs for his people. It’s natural for him to be more concerned about American jobs than the jobs in Liaoning or Guangdong.
But we should also explore how the green energy boom can benefit everyone and how Chinese companies can invest in and be welcomed in Europe and North America.
For instance, Tesla was invited to come to China. China invited Tesla to a large extent to create fair competition in the electric car market in China. It helped shape BYD, Hongqi, Geely, and all the other Chinese brands. Thus, the US should invite Chinese companies to invest in America, shaping the competition in the American market. Then maybe American companies would be more cost-competitive as well.
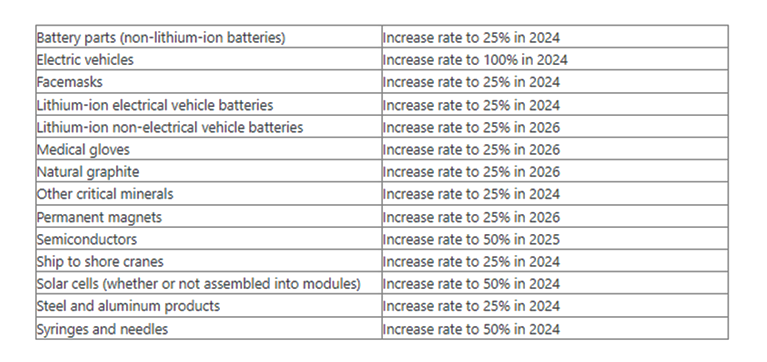
GT: We are now seeing the US government raising tariffs on Chinese EVs, advanced batteries, solar cells, and other goods. What impact will it have on the world if the US government continues to exclude Chinese new energy products?
Solheim: It will obviously slow down the green transformation because China is now the indispensable country for everything green. 60 percent of all green technologies in the world are in China. When it comes to solar energy, maybe the figure is even more than 90 percent. If we want to go solar without China, we can do it, but it will be much more costly. When it’s more costly, it will be slower. And all historical experiences show that if you create closed-down markets and separate markets from different parts of the world, we will all be poorer, including the Americans.
GT: Do you think Europe will follow the latest policies of the US? From your understanding, how does Europe view China’s green manufacturing capacity – is it more inclined toward cooperation or vigilance?
Solheim: That’s obviously a similar discussion in Europe. I don’t think Europe will automatically follow the US, but there is a concern with jobs in Europe. China can help in that discussion in two ways.
First, making very clear that China is ready to invest in other markets where Chinese companies are, and to create jobs in Europe.
Let me give one example. Very recently, I visited Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL) in Ningde, Fujian Province, the world’s largest battery maker for electric vehicles. A Tesla normally comes with a CATL battery. But the guys at CATL repeatedly told me that one of the reasons why they have grown so big was the support from BMW in the early days. BMW was a very demanding customer, it helped with technology and was a partner in the rise of CATL. That’s exactly what we want to see – companies working together across borders. And now when Chinese companies tend to have the highest quality and the best technology, they should work with companies in India, Africa, Latin America, and also Europe to share their knowledge and experience so that we can all benefit from the green transformation.