‘Arise Africa, Roar China’ is an important book exploring aspects of the historic linkages between progressive African Americans and the Chinese revolution. Published by the University of North Carolina Press in December 2021, the author, Dr. Gao Yunxiang was born and grew up in the People’s Republic of China and is now Professor of History at Canada’s Toronto Metropolitan University. Her book explores the close relationships between three of the most famous twentieth-century African Americans, W. E. B. Du Bois, Paul Robeson, and Langston Hughes, and their little-known Chinese allies during World War II and the Cold War—journalist, musician, and Christian activist Liu Liangmo, and Sino-Caribbean dancer-choreographer Sylvia Si-lan Chen. Charting a new path in the study of Sino-American relations, Gao Yunxiang foregrounds African Americans, combining the study of Black internationalism and the experiences of Chinese Americans with a transpacific narrative and an understanding of the global remaking of China’s modern popular culture and politics. Dr. Gao reveals interactions between Chinese and African American progressives that predate those that flourished in the 1960s and early 1970s in particular.
To introduce the book, we are pleased to republish this two-part interview with Dr. Gao conducted for the popular Sixth Tone website by Liu Zifeng, a doctoral candidate in Africana Studies at Cornell University in the US.
Liu Zifeng: How did you get interested in the ties between Chinese and African Americans? What inspired you to write “Arise Africa! Roar China!”?
Gao Yunxiang: While conducting research on my first book, “Sporting Gender,” I came across laudatory articles on W. E. B. Du Bois and Shirley Graham Du Bois in The People’s Daily. They reminded me of some things I read in my childhood: specifically, an old newspaper article and a propaganda poster.
In my childhood home in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, our ceiling was a flat lattice of wooden boards pasted over with old newspapers purchased in bulk. After I learned to read and write, I was confronted every night by a headline pasted right above my pillow — until it was covered by a new layer of old newspapers the following Lunar New Year. Since I read those words daily, they were inscribed in my brain: “Robert Williams and Madam Du Bois Fervently Acclaim Chairman Mao’s Statement Supporting Black Americans’ Struggle Against Violent Repression.”
That title is in turn connected to the memory of a poster that hung in our little classroom for 18 students between grades one to three. Advocating solidarity in the liberation struggle, the poster featured indignant men and women of various ethnicities, all dressed in vibrant clothing and charging forward, with a muscular Black man holding a gun at the center.
“Sporting Gender” was released in 2013. Around the same time, I published an article in the journal Du Bois Review that explored how W. E. B. and Shirley Graham Du Bois’ endeavors in Maoist China added new dimensions to Sino-American relations and Black internationalism. Working on that article, I naturally came across Paul Robeson, a close ally of the Du Boises. Then, while researching the fascinating yet unknown dynamics between Paul Robeson and China, I came across his Chinese allies: Liu Liangmo and Sylvia Si-lan Chen.
Of course, I was immediately curious about who they were. While looking into Chen, I learned that Langston Hughes was her lover. So, I traced these figures just like interlocked chains.
Liu: What attracted African American intellectuals, artists, and activists to China? How did they encounter Chinese and China? What were their impressions of these encounters?
Gao: Solidarity between people of color globally and their shared destiny of anti-racism and anti-colonialism attracted these figures’ attention to China. As a minority facing overwhelming state-imposed systematic racism and white supremacy, Black intellectuals and activists looked toward the similarly oppressed China for inspiration and strength.
These figures’ ties with leftist Chinese and China were built on a profound emotional and intellectual foundation. They shared a faith in Sino-Afro racial, linguistic, philosophical, and artistic kinship. Hughes observed Chinese to be “a very jolly people, much like colored folks at home”; Du Bois lauded Chinese as “my physical cousins.”
Both Du Bois and Robeson consistently articulated the linkage between African and Chinese civilizations and cited famous Chinese cultural giants such as Confucius and Laozi to argue for the sophistication of African civilization, counter negative stereotypes associated with perceived African “primitivism,” and debunk white supremacism.
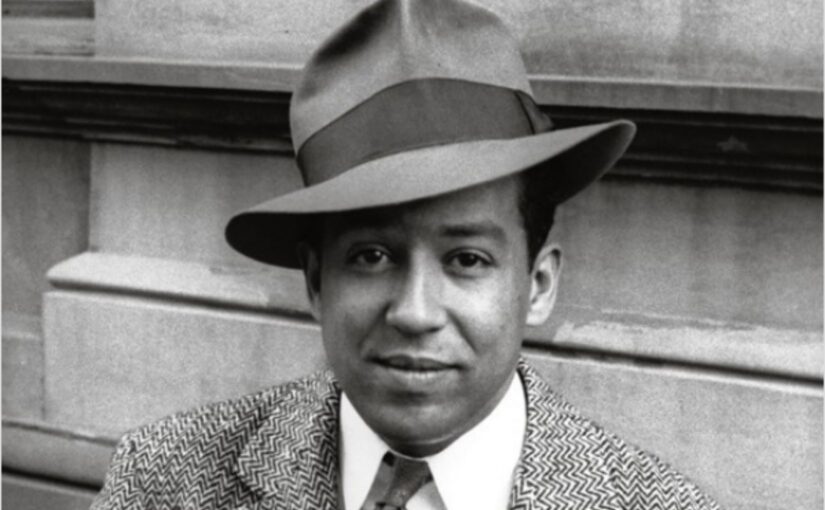
Cultural kinship necessitated a political alliance. By embracing China’s revolutions as vehicles for the social and economic uplift of nonwhites, Black intellectuals directly linked the struggles of African Americans with those of nationalist Chinese. Hughes’ 1933 journey to “incredible” Shanghai made him the first Black intellectual celebrity to set foot on Chinese soil. He was profoundly sympathetic to China’s suffering under colonial oppression, especially Japan’s latest aggressions. Hughes would pen a passionate poem, “Roar, China!” following Japan’s full-scale invasion of China in 1937, lionizing China’s resistance.
The Communist victory in 1949 made China a pillar of nonwhite peoples’ revolutionary struggles and a model for millions to beat colonialism. Robeson romantically imagined that the nonwhite world would view the rising China as a “new star of the East… pointing the way out from imperialist enslavement to independence and equality. China has shown the way.”
During his epic China trip in 1959, Du Bois repeatedly proclaimed Chinese and African dignity and unity in the face of Western racism, colonialism, and capitalism: “Africa, Arise, and stand straight, speak and think! Turn from the West and your slavery and humiliation for the last 500 years and face the rising sun … China is flesh of your flesh and blood of your blood.” He predicted that the “darker world” would adopt socialism as “the only answer to the color line,” and that the status of African Americans would thereby be elevated.
Despite withdrawing from radicalism due to anti-Communist hysteria in the United States, Hughes nevertheless remained confident of the power of the People’s Republic of China. His suppressed inspiration, drawn from the Chinese Communist Party, resurfaced in his fury at the brutal racial violence African Americans suffered. “Birmingham Sunday,” Hughes’ eulogy to the four Black girls killed in the dynamiting of the 16th Street Baptist Church in Birmingham, Alabama, on Sunday, September 15, 1963, connected his rage with the rage one once felt by oppressed Chinese.
Liu: How about the Chinese intellectuals and activists you profile? Who were they? What prompted them to reach out to African Americans and what did they do to build Sino-Black solidarity?
Gao: The Chinese intelligentsia had, through literature and drama, long connected the shared “enslavement” of the Chinese nation as a semi-colony state and the enslavement of African Americans. In the introduction to their 1901 translation of Harriet Beecher Stowe’s “Uncle Tom’s Cabin,” Lin Shu and Wei Yi argue that the tortures “yellow” people faced were even worse than those endured by Black Americans. Chinese people needed to read the book, Liu and Wei write, because “slavery is looming for our race. We had to yell and scream to wake up the public.”
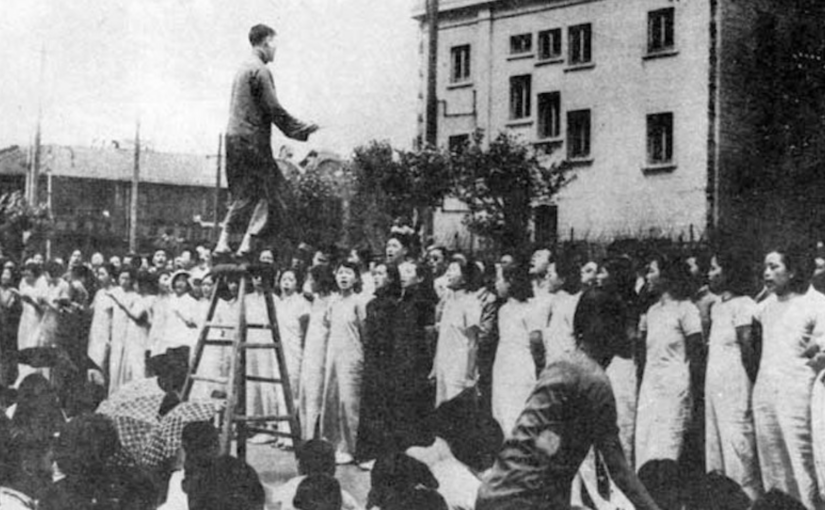
In the face of harassment by the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the Immigration and Naturalization Service, as well as racial terror and segregation, Liu Liangmo’s and Sylvia Si-Lan Chen’s brave journeys to the United States brought Sino–African American cultural alliances into new historical settings. Liu was a talented musician, prolific journalist, and Christian activist who initiated the trans-Pacific mass singing movement for war mobilization during World War II. He was a pioneer among Chinese for his close collaboration with African Americans, lauding Black greatness without reservation and later facilitating the reception of the Du Boises and Robeson in the People’s Republic. Among the numerous areas in which Liu and Robeson collaborated, they helped to globalize the signature piece of the mass singing movement: “Chee Lai” or “March of the Volunteers.”
In 1941, Robeson, Liu, and the Chinese People’s Chorus, a group Liu had organized among members of the Chinese Hand Laundry Alliance in New York City’s Chinatown, recorded an album for Keynote Records titled, “Chee Lai: Songs of New China.” Liu’s liner notes for the album relay that he saw the collaboration as “a strong token of solidarity between the Chinese and the Negro People.”
Robeson’s notes read: “Chee Lai! (Arise!) is on the lips of millions of Chinese today, a sort of unofficial anthem, I am told, typifying the unconquerable spirit of this people. It is a pleasure and a privilege to sing both this song of modern composition and the old folk songs to which a nation in struggle has put new words.”
The song would be adopted as the national anthem of the People’s Republic of China in 1949.
Chen was the world’s first “modern Chinese/Soviet dancer-choreographer” with an international reputation, according to contemporary American media accounts. She was a daughter of Eugene Chen, China’s foreign minister in the 1920s, and his French Creole wife. She was also a cousin of Dai Ailian, the acclaimed “mother of China’s modern dance.”
The Chens and Dai were all born in Trinidad and barely spoke Chinese. Chen encountered Hughes romantically in Moscow, fanning his interest in China, connecting him with the international Communist network, and helping to propel him into Shanghai’s leftist cultural circles. Chen captured the fanciful imaginations of Hughes and Robeson, who saw her as personifying the “perfect” union of Black and Chinese. Meanwhile, her own journey to choreograph and dance ethnicity, war, and revolution around the globe illustrates the complex racial and political twists of such an interracial union.
Liu: How did the African American intellectuals profiled in your book shape Chinese perceptions of Blackness and visions of the world order? And how did China’s engagement with the Africana world, at least in the cases of Liu Liangmo and Sylvia Si-Lan Chen, inform African American understandings of Chinese politics and culture and Black radical thought more generally?
Gao: W.E.B. Du Bois, Langston Hughes, and Paul Robeson’s presence in China and their alliances with Chinese sojourners helped facilitate a shift in the dynamics of Pan-Africanism and Pan-Asianism and ultimately inspired the “color line” of Mao Zedong’s Third World theory.
The transformative process started with gradual changes in the images of Blacks in the Republic of China (1912-1949). Stung by its humiliating reputation as the “sick man of Asia” and alarmed by Nazi racism and Japan’s imperialist ambitions, China was acutely frustrated by the repeated defeats of Chinese athletes at the 1932 and 1936 Olympics. Thus, Chinese media celebrated the “natural” physical prowess of the boxer Joe Louis and track-and field athlete Jesse Owens on behalf of the world’s people of color.
The front cover of an issue of China’s leading cartoon magazine, Modern Sketch, devoted to the 1936 Olympics, drew inspiration from Owens’s triumph. The magazine’s back cover featured a drawing of a muscular Black woman resembling the American chanteuse Josephine Baker, clad in a banana skirt, captioned, “Victory of Colored People at the Olympics.”
Those two images exemplified Chinese portraiture of African Americans. Du Bois, who visited China around that time, announced that the race “must be represented, not only in sports, but in science, in literature, and in art.” Jazz musicians in nightclubs, who were dismissed as “foreign musical instrument devils” — yangqin gui — or else caricatured in advertisements for toothpaste and white towels, dominated Black representation in Republican Chinese media. The presence of Du Bois, Hughes, and Robeson, whose intellectual capacities Chinese critics described as “genius,” started to alter such stereotypes.
During his trip to Shanghai, Hughes was quickly embraced by the city’s leftist cultural circles, led by the author Lu Xun. Their magazines hailed him as the “first established Black revolutionary writer,” who was “howling and struggling for the oppressed races.” Hughes’ visit triggered ongoing interest in his work and Black literature in China.
The final step of connecting Blackness with revolution occurred during the People’s Republic of China. The narrative on the globally famous Robeson was quickly transformed from that of an exotic entertainer to a heroic model and inspiration for the country’s socialist citizens. He was introduced in state media as “the Black King of Songs” for the oppressed masses in the world, who “embodied the perfect marriage between art and politics.”
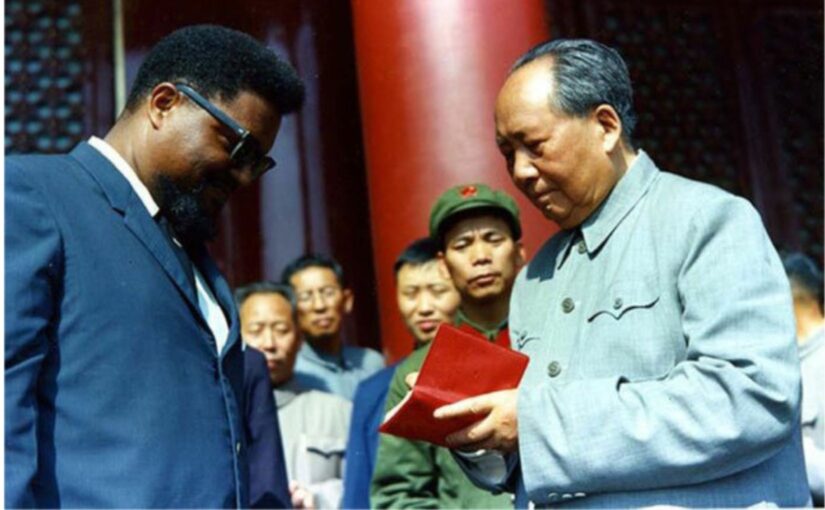
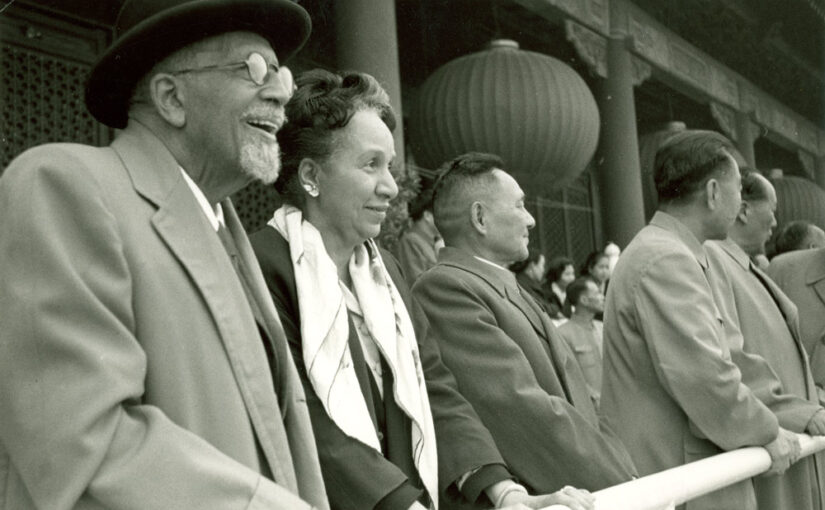
After Du Bois shifted his favorable gaze from Japan to the People’s Republic of China as the new pillar of the colored world, he was treated as an icon by a China aspiring to leadership in the “Third World.” During their visits, he and his wife received unprecedented state hospitality. The couple frequently rubbed shoulders with China’s top leadership, became the first Westerners to grace the Tiananmen Square podium during the country’s National Day celebrations, and frequently occupied the front pages of major newspapers. Du Bois’ birthdays were celebrated as major state events.
Liu and Chen, meanwhile, linked the burning issues facing Chinese Americans and African Americans — such as the poll tax, the Chinese Exclusion Act, Jim Crow laws, and the lynching of African Americans — while urging their abolition.
Liu Zifeng: How did the Cold War international order, Sino-Soviet relations, and shifts in Chinese and U.S. foreign policy impact relations between Chinese and African Americans?
Gao Yunxiang: Following its rough birth amid the intensifying Cold War atmosphere, the infant People’s Republic of China was forced to confront a superpower armed with nuclear weapons in the Korean War. By this point, the singer, actor, and activist Paul Robeson was enshrined as a fearless and reliable friend of China, and for Robeson, China was a strong source of support that he sorely needed.
April 20, 1949 marked the start of Robeson’s political downfall in the United States. On that day, he famously told the International Congress for Peace in Paris that it was “unthinkable that American Negroes would go to war on behalf of those who have oppressed us for generations against the Soviet Union.” That statement quickly drew widespread condemnation, including from Jackie Robinson, the famous African American baseball star, whom Robeson had helped to integrate the game.
Joining W.E.B. Du Bois in standing firmly behind Robeson was the Chinese Communist Party. The People’s Daily condemned Robinson and defended Robeson. The paper reported Robeson’s speech, highlighting the standing ovation the star received from the event’s 2,000 attendees, including Nobel Laureate and nuclear scientist Frederic Joliot-Curie and Robeson’s friend, the artist Pablo Picasso. Treating the organized regional and world peace movement as a powerful popular rebuke of U.S. involvement in China’s Civil War and later the Korean War, Chinese state media reported intensively on the involvement of Du Bois and Paul Robeson in the pacifist movement.
The United States quickly accelerated its attacks on Robeson. The most significant and ugliest example was the so-called Peekskill riots, in which right-wing mobs brutally attacked a Robeson concert in August 1949. Soon, the U.S. State Department cancelled Robeson’s passport and stalled his brilliant career. As is well documented in both Robeson’s writings and Chinese state media coverage, Robeson and the People’s Republic lent each other unyielding support during their most trying moments.
By the late 1950s, in the wake of the disastrous Great Leap Forward, China had immediate reasons to welcome public support from African American cultural giants. The CCP needed a new domestic perspective to reinvigorate the revolution and socialize the nation. In addition, it required new diplomatic defenders and tactics as it contested Soviet dominance of world communism and aspired to leadership of the “Third World” that bound the destinies of China with former agricultural colonies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
The CCP was already reaching out to Africa, but the newly independent African states met Chinese overtures with caution and reserve. The stature of these African American figures among the African diaspora helped China open doors for alliances across the continent. Du Bois’ reputation and endorsement particularly meant a great deal. Chinese outreach to Africa through diplomatic exchanges, aid, and propaganda peaked following the Du Boises’ 1959 visit to China. For diplomatic and economic reasons, China continued to maintain a large presence in Africa, which the Du Boises helped to foster.
During the 1960s, Mao Zedong was interested in contacts with radical Blacks, who he valorized as true revolutionaries. Influential Black activist Robert Williams, author of “Negroes with Guns,” was mentioned in a People’s Daily headline plastered on the ceiling of my childhood bedroom, for instance. At the same time, Black Americans were impressed by Mao’s anti-American imperialism as well as his emphasis on violent struggles and cultural change as a revolutionary force.
Liu: As often happens in cases of transnational exchange, the intellectual and cultural interactions between China and African America that you chart were fraught with misunderstandings, ambiguity, and conflict. What were some of the complexities and contradictions of the internationalist politics of the five central figures in your book?
Gao: Caught in between the murky, sometimes treacherous, and shifting trans-Pacific political and ideological waters, all five citizens of the world I profile — W.E.B. Du Bois, Paul Robeson, Langston Hughes, Liu Liangmo, and Sylvia Si-lan Chen — experienced their share of ambiguity and conflict. For instance, in 1962, state media and publishers in the People’s Republic of China suddenly fell silent on Robeson, who had been promoted as a heroic revolutionary model for China’s socialist citizens throughout the 1950s. After the Sino-Soviet split came into the open, Robeson’s position of advocating for peaceful coexistence fell on the wrong side of Chinese politics amid a shift in dynamics between the trans-Pacific powers.
The official press took an alternative approach toward Hughes. Outlets awkwardly remained silent on Hughes’s public renunciation of his radical past at the peak of McCarthyism and the Korean War; instead, they fixed their gaze on the writer he was in the 1930s, an “established Black revolutionary writer,” as if he were preserved in a time capsule. Liu and Chen, meanwhile, were marginalized and even attacked during the radical Maoist years by a regime they had long idealized.
W.E.B Du Bois’ treatment of imperial Japan — which brutalized China and Asia — as a pillar of “the darker word” turned out to be the most controversial. Du Bois visited the segregated treaty port of Shanghai in 1936. Pampered by the Japanese authorities, he stayed at the luxurious Cathay Hotel on the Bund. At the University of Shanghai, Du Bois “occupied a seat on the dais,” listening as a Rockefeller Foundation representative spoke about scholarships to the United States.
“I said to the president that I should like to talk to a group of Chinese and discuss frankly racial and social matters,” Du Bois recalled. He soon “plunged…recklessly” into a luncheon at the Chinese Bankers’ Club at 59 Hong Kong Road on November 30. He wanted to know, in his own words, “Why is it that you (Chinese) hate Japan more than Europe when you have suffered more from England, France, and Germany than from Japan?” If Japan and China worked together, Du Bois continued, perhaps Europe could be eliminated permanently from Asia. Du Bois calmly reported, “There ensured a considerable silence, in which I joined.”
His dismayed hosts responded that whatever problems China suffered, Japan’s militarism hindered any progress. Unconvinced, Du Bois commented later that “the most disconcerting thing about Asia is the burning hatred of China and Japan (for each other).” As he sailed from Shanghai aboard the S. S. Shanghai Mari to Nagasaki on December 1, 1936, Du Bois hurled a final insult, claiming that the Chinese Nationalists were “Asian Uncle Toms,” likening them to the willing Black menials of white racism in the United States.
Du Bois repeated his belief in the virtues of Japanese rule and firmly urged a Sino-Japanese alliance, which would “save the world for the darker races.” He steadfastly maintained such views even after Japanese forces occupied Beiping (today’s Beijing) and Shanghai. To the news of the Nanjing Massacre, Japan’s genocidal occupation of China’s then-capital in late 1937 and early 1938, Du Bois responded that few of the white Americans expressing horror at the killing had said much about Italy’s recent depredations in Ethiopia.
Liu: What lessons do the stories recounted in your book offer for understanding China-U.S. relations?
Gao: While most scholarship on Sino-American relations treats the United States as default white, “Arise, Africa! Roar, China!” cuts a new path by foregrounding African Americans. It allows us to reimagine Sino-American relations by decentering Henry Kissinger and Richard Nixon in the discourse, understanding Afro-Asian history as central to world history, and focusing on global anti-imperialism and popular movements which are still relevant today. My book combines the study of Black internationalism and the experiences of China and Chinese Americans with a trans-Pacific narrative. It reveals earlier and widespread interactions between Chinese and Black leftist figures prior to the better-known alliance between Black radicals and Maoist China in the 1960s.
It also shows the global remaking of China’s modern popular culture and politics. The book traces China’s transnational entanglements even during periods when the nation has commonly been regarded as insular and unconnected to the wider world.
The intertwined lives of these five citizens of the world, usually perceived as inhabiting non-overlapping domains, stand as powerful counters to narratives that foreground racism and alienation. Their endeavors across racial, national, cultural, and linguistic boundaries illustrate that the world always remains connected despite political, legal, immigration, and diplomatic hurdles. Their stories offer a view into the power and potential of Black internationalism and Sino–African American collaboration. “Arise, Africa!” and “Roar, China!” as articulated by Du Bois and Hughes, respectively, match the shared struggles of a nation and a nation-within-a-nation. Their power and promise resonate to this day.