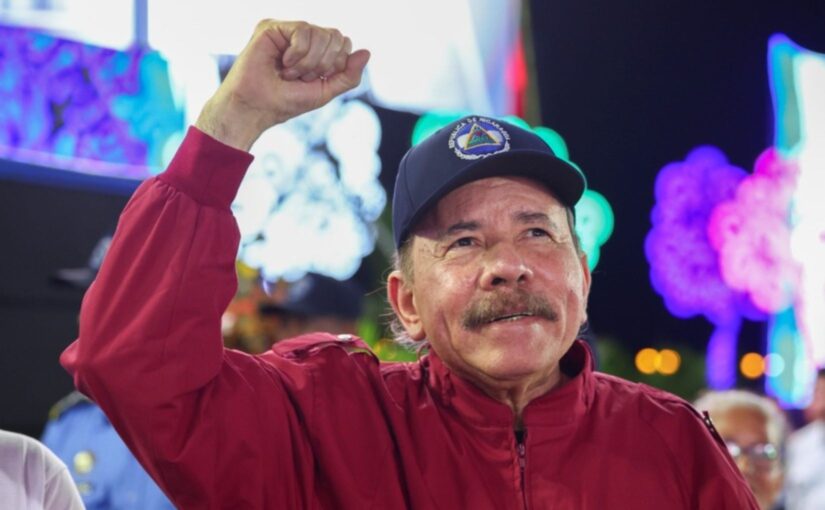
On July 15, Nicaraguan President Daniel Ortega and Vice President Rosario Murillo attended a special ceremony in the capital Managua to hand over a fleet of Chinese buses produced by the Yutong company to the city’s transport cooperatives.
“Today,” Ortega declared, “we are delivering these buses so that they contribute to the transportation of families, of children going to school, of young people going to school, going to university; of workers, women, doctors, teachers, of all sectors of Nicaraguan society, who use collective transport.”
A special day had been chosen: “Today, July 15th, is the day our Brother Julio Buitrago, a young man, fell in combat. Julio was in college but went on to combat with the Sandinista Front, and the feat, the heroism, of Julio, who fell in combat 55 years ago today, on July 15th 1969, is well known. He was alone! He was surrounded by 300 National Guard, trained by the Yankees, they brought small tanks, they brought airplanes, and he resisted until his last cartridge… And in tribute to Julio we make this handover on this day, in tribute to Julio who represents Nicaragua’s youth, giving their lives for Nicaragua, fighting for Nicaragua.”
Ortega took the occasion to outline in some detail the long history of solidarity between the Nicaraguan and Chinese revolutions. Referring to a speech just delivered by China’s Ambassador to Nicaragua, he continued: “Our relations with China are historic. Ambassador Chen Xi recalled the years of the triumph of China’s revolution, and they will be commemorating now 75 and us 45. What does this mean? That it took 30 years for the triumph of the Sandinista revolution to follow on, and before the triumph of the Nicaraguan revolution was the triumph of the Cuban revolution, which was immediately intertwined with the People’s Republic of China, when the great Chairman Mao Zedong was at the head of the People’s Republic of China.
“When we were fighting, from the 1960s onwards, against the tyranny of Somoza, we maintained links with the leaders of the Chinese party; compañeras and compañeros of the Sandinista Front traveled there, to China, in those years. And naturally we were inspired by the Chinese revolution, a revolution that had an impact on the world, with such an immense territory and with a division in the country, and the ability that the Chinese leadership, headed by Mao, displayed in uniting that great nation, where there were a great many differences between the provinces. They had to be united, and he united them.
“Then the Chinese revolution came to grow, it came to advance, facing counter-revolutions, and later the Chinese people’s revolution managed to take a great leap forward, such that now, with President Xi Jinping, much wider doors are opening for humanity.”
China, Ortega said, “has been fulfilling its principles, which are revolutionary principles, they are the principles of the Chinese Communist Party, with which we have always maintained relations. Tomás [Tomás Borge, a co-founder and central leader of the Sandinista National Liberation Front, FSLN] was there, in China, in various seminars held there in China in which leaders of the revolutionary parties of Central America took part. Victor Tirado [another historic Sandinista Commandante] had also been there before.
“And China today, is really serving as a compass, pointing the way which other nations share as well, that Planet Earth cannot continue to live under the boot of empires which accumulate wealth at the expense of developing peoples, crushing them, invading them, murdering them. This has to change, and it will surely have to change, because every day we find more countries defending these positions.”
Having praised the cultural performances at the celebration from indigenous and Afro-descendant peoples on his country’s Caribbean coast, Ortega referred to the next tranche of 1,000 buses that will be delivered from China, saying that, “we guarantee some buses for the Caribbean coast, so that they reach Bluefields and reach Bilwi, so that they reach the Mines Region; that is, that the embrace of solidarity from the Chinese people reaches the Miskito peoples, the Ramas, the Afro-descendant population, the Mayagna, the Garifuna. May this embrace of solidarity from the Chinese people reach all these communities, because now the highways are there, and the highways are still advancing. So, there should be no problem now for these buses to circulate on the Caribbean coast.”
He went on to recall his own state visit to China in 1986, where, “we managed to meet as the brothers and sisters that we are.” However, “in the 1990s the neoliberal politicians imposed by the Gringos came along, and the first thing they did was break off relations with the People’s Republic of China.”
After the struggle against three consecutive neoliberal governments, “we returned to government, always in communication with the People’s Republic of China, looking for the moment when we could normalise relations again. We have been united in our struggles, in the battles that the Chinese people have been waging to improve their conditions, to strengthen themselves in all fields, to stand in solidarity with the peoples of Asia, Africa, Latin America, with the peoples of the world.”
Four days after this speech, on July 19, Nicaragua celebrated the 45th anniversary of the victory of the Sandinista people’s revolution. Tens of thousands of Nicaraguans were joined by government delegations from numerous countries, including Algeria, Angola, Belarus, Burkina Faso, China, Cote d’Ivoire, Cuba, Ghana, Honduras, Iran, Kuwait, South Ossetia, Palestine, Qatar, Russia, South Africa, United Arab Emirates, Venezuela, Vietnam and Zimbabwe, along with solidarity delegations from numerous other countries, to hear President Ortega make another important speech. A special guest was the legendary Palestinian revolutionary Leila Khaled.
Having referred to the historic and decisive support rendered by the Soviet Union in the first period of building a new society in Nicaragua, and to Russia’s current struggle against the revival of Nazism in Ukraine, Ortega continued:
“And there is another nation with which we have also had historical relations, the People’s Republic of China, which has been bringing progress, benefits and development to the world’s peoples who were colonised and who became independent, but who were then subjugated under the boot of the interests of the powers that had colonised them, leaving those peoples in poverty, with people in misery, people going hungry, people in illiteracy, with infant mortality, in Africa, in Asia. And the People’s Republic of China has been developing a policy bringing benefits to developing countries, without setting any conditions.
“So now the great powers grouped in NATO already have an incipient war which is in the phase of them preparing their own peoples for what they call a threat; that Russia and China are a threat, but then, too, there are the BRICS, where there is India, and they say they too are a threat. That is to say, everything that is a coming together of nations, of countries, where sovereignty is respected, where they reach agreements to achieve better conditions for their peoples, they see as a threat, because the imperialists are used to occupying by force, and then dominating and murdering; and then pointing accusing fingers at us.”
The following articles were originally published by Tortilla con Sal.
Continue reading Daniel Ortega: China is bringing progress and benefit to the peoples of the world