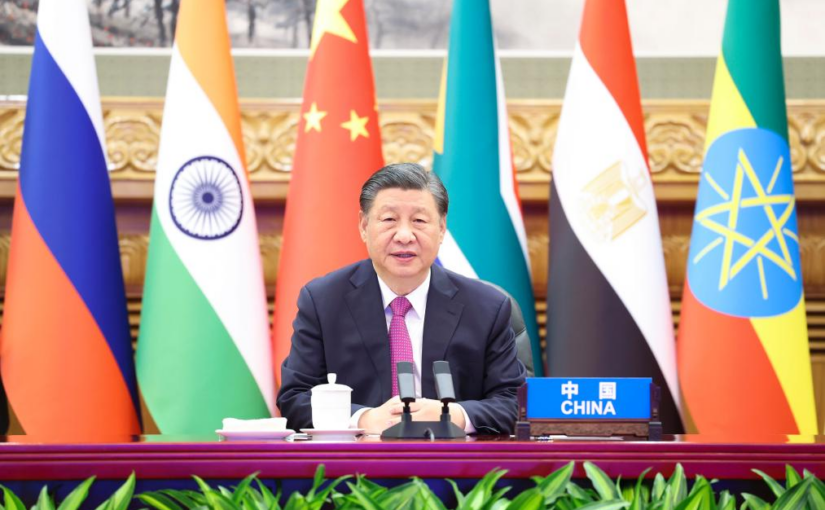
On November 21, Chinese President Xi Jinping addressed an extraordinary joint meeting of the leaders of the BRICS countries, along with the leaders of those countries who have been invited to join the cooperation mechanism from January 1, 2024, called to discuss the situation in the Middle East with particular reference to Gaza. The meeting was held virtually and was initiated by the current chair of BRICS, President Cyril Ramaphosa of the Republic of South Africa.
In his address to the meeting, President Xi said that China is gravely concerned that the current conflict is causing enormous civilian casualties and a humanitarian disaster. He stressed that the collective punishment of people in Gaza in the form of forced transfer or water, electricity and fuel deprivation must stop and continued:
“The root cause of the Palestinian-Israeli situation is the fact that the right of the Palestinian people to statehood, their right to existence, and their right of return have long been ignored. I have emphasised on many occasions that the only viable way to break the cycle of Palestinian-Israeli conflict lies in the two-state solution, in the restoration of the legitimate national rights of Palestine, and in the establishment of an independent State of Palestine. There can be no sustainable peace and security in the Middle East without a just solution to the question of Palestine. China calls for early convening of an international peace conference that is more authoritative to build international consensus for peace and work toward an early solution to the question of Palestine that is comprehensive, just and sustainable.”
He also outlined the humanitarian assistance that China has so far provided to the Palestinian people in the current situation, adding that, “China will provide more supplies and assistance according to the needs of the people in Gaza.”
We reprint the full text of President Xi’s remarks below. They were originally published by the Xinhua News Agency.
Working Toward a Ceasefire and Realizing Lasting Peace and Sustainable Security
Remarks by H.E. Xi Jinping
President of the People’s Republic of China
At the Extraordinary Joint Meeting of BRICS Leaders
And Leaders of Invited BRICS Members
On the Situation in the Middle East with Particular Reference to Gaza
November 21, 2023
Your Excellency President Cyril Ramaphosa,
Colleagues,
This is our first summit since the expansion of BRICS. Before I speak about the issue of our discussion, I wish to extend a warm welcome to leaders of new BRICS members and express my thanks to President Ramaphosa and the South African government for your efforts that have made our meeting possible. Given the current circumstances, it is very timely and very important that we meet and speak up for justice and for peace on the Palestinian-Israeli issue.
The conflict in Gaza is raging on into its second month. China is gravely concerned that the conflict is causing enormous civilian casualties and a humanitarian disaster, and tends to expand and spill over. China believes that the following is urgent and imperative: First, the parties to the conflict must end hostilities and achieve a ceasefire immediately, stop all violence and attacks against civilians, release civilians held captive, and act to prevent loss of more lives and spare people from more miseries. Second, humanitarian corridors must be kept secure and unimpeded, and more humanitarian assistance should be provided to the population in Gaza. The collective punishment of people in Gaza in the form of forced transfer or water, electricity and fuel deprivation must stop. Third, the international community must act with practical measures to prevent the conflict from spilling over and endangering stability in the Middle East as a whole. China supports the resolution adopted at the emergency special session of the U.N. General Assembly on October 27. The U.N. Security Council under China’s presidency has adopted Resolution 2712. All the parties must act to deliver on these resolutions through concrete measures on the ground.
The root cause of the Palestinian-Israeli situation is the fact that the right of the Palestinian people to statehood, their right to existence, and their right of return have long been ignored. I have emphasized on many occasions that the only viable way to break the cycle of Palestinian-Israeli conflict lies in the two-state solution, in the restoration of the legitimate national rights of Palestine, and in the establishment of an independent State of Palestine. There can be no sustainable peace and security in the Middle East without a just solution to the question of Palestine. China calls for early convening of an international peace conference that is more authoritative to build international consensus for peace and work toward an early solution to the question of Palestine that is comprehensive, just and sustainable.
Since the outbreak of the latest Palestinian-Israeli conflict, China has been working actively to promote peace talks and a ceasefire. China has provided humanitarian assistance to help ease the humanitarian plight in Gaza. This includes USD 2 million of emergency humanitarian assistance provided through the Palestinian National Authority and U.N. agencies, and emergency humanitarian supplies worth RMB 15 million, such as food and medicine, to the Gaza Strip with the help of Egypt. China will provide more supplies and assistance according to the needs of the people in Gaza. At the U.N. Security Council, China has acted in its capacity as president to facilitate the adoption of the resolution, which calls for extended humanitarian pauses and corridors, the protection of civilians, and the provision of humanitarian assistance.
Colleagues,
The BRICS cooperation mechanism is an important platform for emerging markets and developing countries to strengthen solidarity and cooperation and safeguard common interests. Our meeting today to coordinate positions and actions on the Palestinian-Israeli conflict marks a good start for greater BRICS cooperation following its enlargement. China commends South Africa for its significant contribution as BRICS chair to advancing BRICS development. As Russia will take over BRICS chairmanship next year, China stands ready to work with other members to jointly support Russia’s work as the chair and usher in a new era for BRICS cooperation.
Thank you.